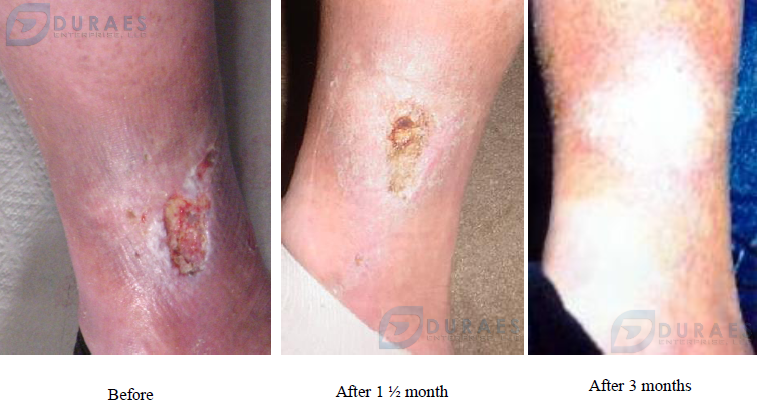
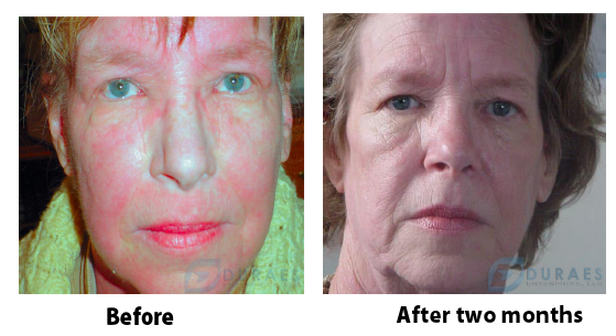
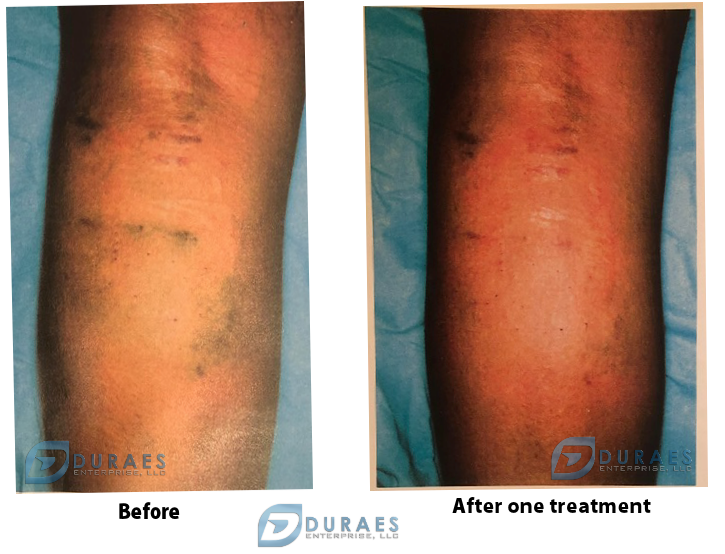
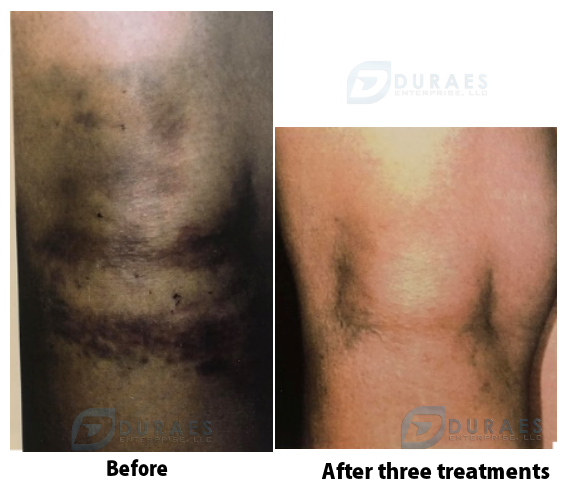
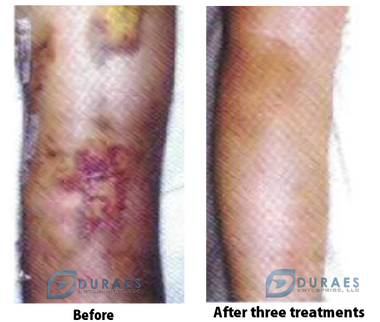
Case Studies
Our products have been proven and concepts have been published in the Textbook of Natural Medicine
What is BALNEOTHERAPY?
BALNEOTHERAPY: The use of baths in the treatment of disease
BALNEOLOGY: The Arts and Sciences of Medicinal Bathing
- Involves the application of hot or cold water to the body.
- Such includes the use of baths, peloids, and other natural substances as well as various climatic elements for the prevention and treatment of disease.
PELOID: The pulp of organic and inorganic materials.
Strengthening the Concept
As it is impossible (at the present time) to include all of our studies that we have accumulated over the past few decades, along with those of our fellow practitioners, not to mention the thousands that are documented worldwide, onto this presentation, you’ll find that the few you are about to see quite impressive and informative.
Endocrinological changes after Peat therapeutics
A study of 28 patients diagnosed with immature follicle sterility were divided into three groups. One group of 16 was chosen specifically for impregnation. The other two groups were evaluated for hormonal parameters, in consideration primarily prolactin, FSH, LH, DHEA-S, and estradiol. All patients received three peat baths per week, up to 12 treatments, and were evaluated on the ninth day of the cycle before treatment, and on the ninth day of the cycle 1.8 to 2.4 months following therapy.
Results
FSH was lowered from 8.0 mE/ml to 4.0 mE/ml; LH lowered from 10.0 mE/ml to 6.0 mE/ml; and estradiol elevated from 5.5 pg/ml to 10.0 pg/ml. Also, normalization of progesterone-biosynthesis was noted.
In the group of 16 patients, 11 became pregnant, with one miscarriage. This demonstrates a 68.8% treatment success modality.
References
J. Dietrich. (1994) Ludwig Maximilians University, Munich, Germany.
Dept. of Gynecology, Cure Clinic Ludwigsbad
As it is impossible (at the present time) to include all of our studies that we have accumulated over the past few decades, along with those of our fellow practitioners, not to mention the thousands that are documented worldwide, onto this presentation, you’ll find that the few you are about to see quite impressive and informative.
Endocrinological changes after Peat therapeutics
A study of 28 patients diagnosed with immature follicle sterility were divided into three groups. One group of 16 was chosen specifically for impregnation. The other two groups were evaluated for hormonal parameters, in consideration primarily prolactin, FSH, LH, DHEA-S, and estradiol. All patients received three peat baths per week, up to 12 treatments, and were evaluated on the ninth day of the cycle before treatment, and on the ninth day of the cycle 1.8 to 2.4 months following therapy.
Results
FSH was lowered from 8.0 mE/ml to 4.0 mE/ml; LH lowered from 10.0 mE/ml to 6.0 mE/ml; and estradiol elevated from 5.5 pg/ml to 10.0 pg/ml. Also, normalization of progesterone-biosynthesis was noted.
In the group of 16 patients, 11 became pregnant, with one miscarriage. This demonstrates a 68.8% treatment success modality.
References
J. Dietrich. (1994) Ludwig Maximilians University, Munich, Germany.
Dept. of Gynecology, Cure Clinic Ludwigsbad
Balneologically Activated Skin Functions and their Clinical Evidence
- Each effect of a bath is natural imparted via the skin, which can act as the gateway for bath components and heat. It is known that the skin can respond to this as either a reflex organ with its differentiated sensorium, a metabolic organ, or an immune organ. In this case the bath can cause within the organism a peripheral impairment of functional sequences which are normally homeostatically controlled. These skin responses can effect the total organism by transmitter substances activating helping functions. The efficiency of medical baths can be rationally explained on the basis of these functional sequences, although there still exists an open field for basic research in this area.
- Permeation through, but not the entry into, the stratum corneum is impeded. The stratum corneum is the is the barrier of the integument used against the penetration of substances into the body and against the elimination of substances from the body. The blood levels of the topical application components are hardly significant. Primary effects of bath components take place not via the blood but in the skin.
- The epidermis is a strategically located buffer zone with the ability to reactively defend against penetrated external aggressors through the use of immunological defenses, the lowering of pain perception, the improvement of haemodynamics, and thermal regulation. Stress hormones, such as ACTH, MSH, epinephrine, and endorphin are produced directly by the skin. The use of serial cellular stress reactions to activate self-healing powers in the organism for the treatment of systemic chronical diseases in typical of the balneotherapy and the natural methods of medicine.
- With baths, significantly higher concentrations of minerals and medicaments can be reached in the epidermis than with systemic flooding via the vascular system. It is not possible to achieve the same reactions in the skin with the use of other application forms of these substances.
All of our clinical double blind studies with sulphurated baths, which have been performed, have shown a significant cure effect due to a relevant pain alleviation with non-articular rheumatism and degenerative complaints. This analgetic effect goes beyond the placebo effect with concomitant physical treatment.
References
Prof. Dr. Helmet G. Pratzel Institute for Medical Balneology and Climatology, University of Munich, Germany